SmartMail
An IoT device combining ESP8266, Raspberry Pi, PHP, and MariaDB to create a connected mailbox with servo control, PIR sensor detection, and a responsive web dashboard.
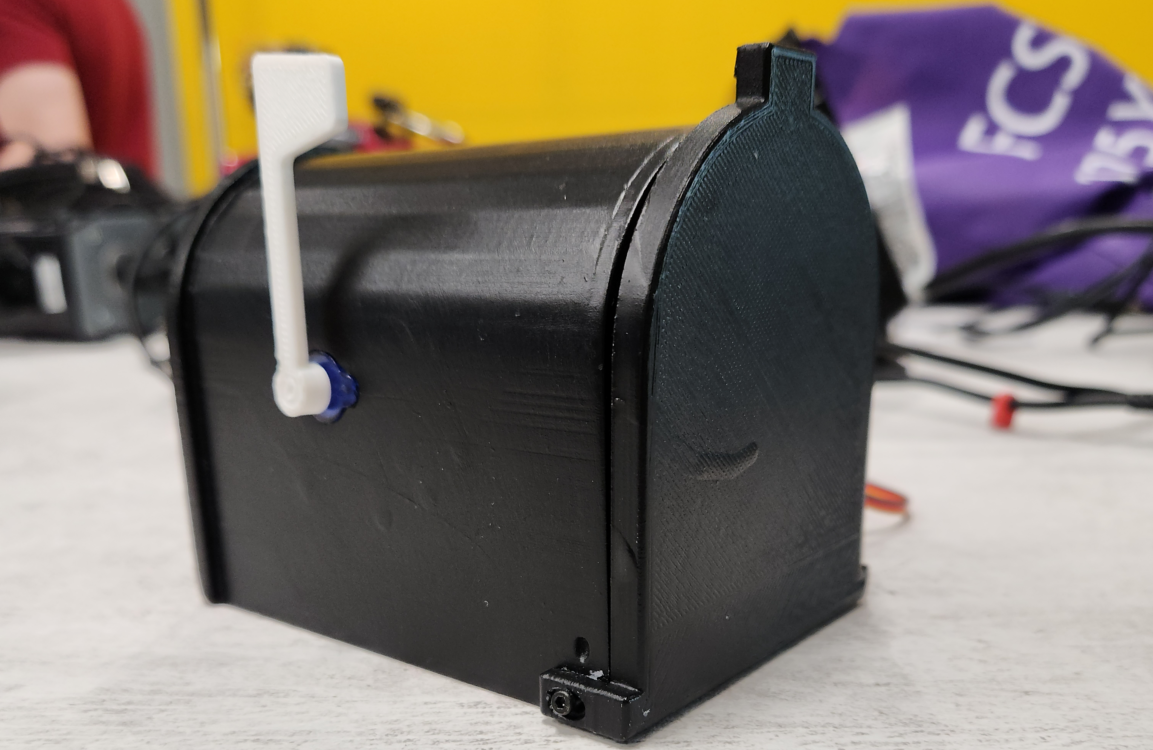

What We Did
For our IoT course, a classmate and I created a “Smart Mailbox” to demonstrate our understanding of sensors, servos, databases, and device-to-device communication. The system uses an ESP8266 to handle hardware control and a Raspberry Pi 4 to host both a MariaDB database and a web dashboard. We wanted a project that was simple enough to complete alongside other coursework, but complex enough to tie together everything we’d learned.
The Pi
Our Raspberry Pi acted as both the web server and the database host. We built the database in MariaDB, storing timestamps and device data whenever mail was detected. The dashboard was built with HTML, PHP, and JavaScript, displaying a table of deliveries and offering buttons to enable/disable the sensor and lock. It also showed live status of the mailbox lock and sensor state.
The Database
Using MariaDB, we created a table called Readings
that stored device names and timestamps.
When motion was detected by the PIR sensor, the ESP8266 posted an entry to the database.
This integration gave us persistent logging of every mailbox interaction and a clear history
accessible from the dashboard.
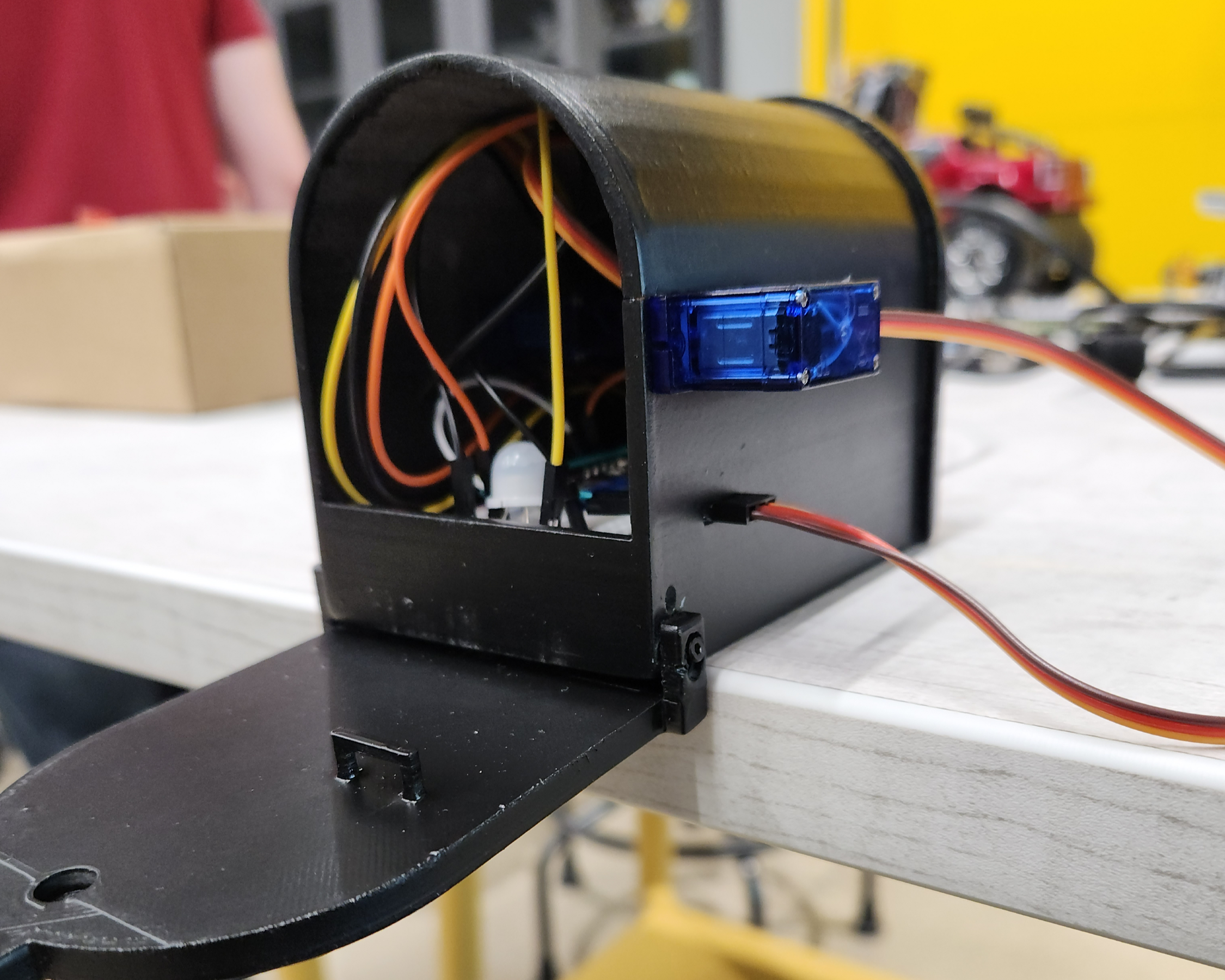
The ESP8266
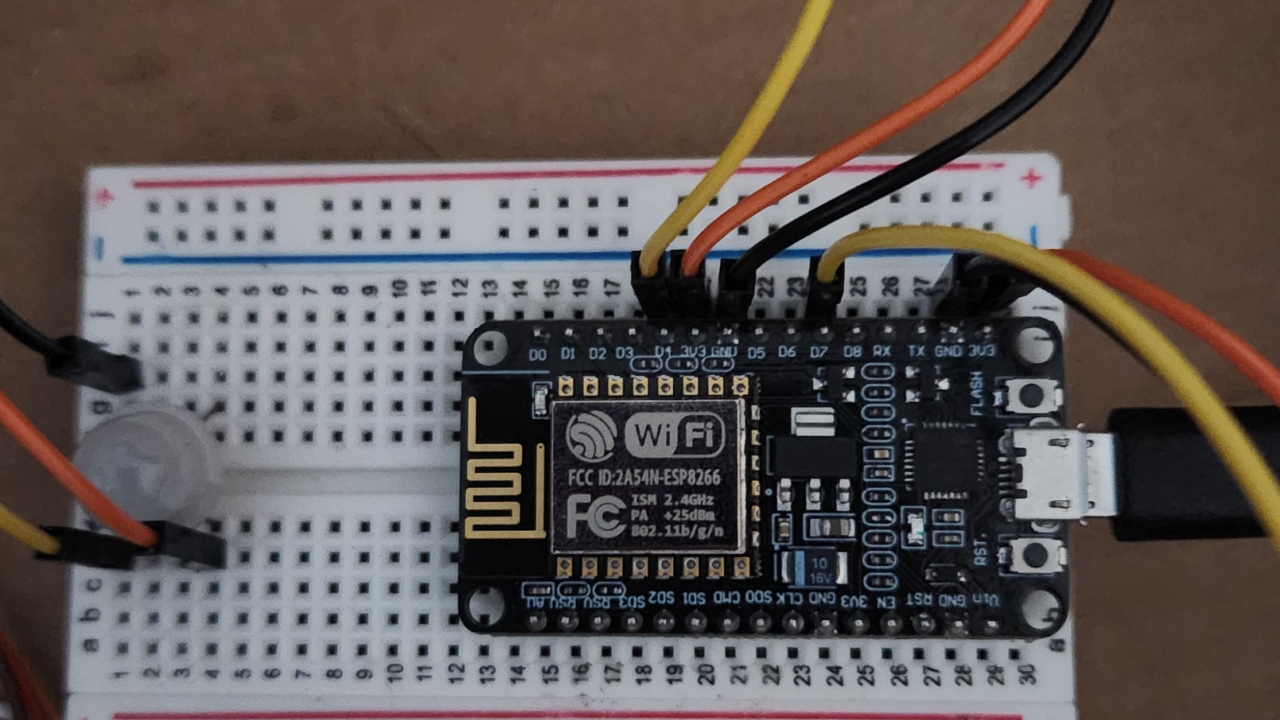
The ESP8266 controlled the PIR sensor and servos, while also making HTTP requests to the Pi. Initially we wired the PIR sensor incorrectly, inverting its signals. With help from our professor, we corrected it and tuned its sensitivity. The firmware, written in the Arduino IDE, let the ESP8266 post sensor data in JSON via POST requests, and fetch updated status via GET requests. This allowed the dashboard to control the lock state remotely.
Video Demo & Conclusion
In our live demo at Baldwin Wallace, the system successfully detected motion, unlocked the mailbox, logged the delivery in MariaDB, and updated the web dashboard. This project gave us hands-on experience with IoT, databases, and embedded hardware, and showed how multiple systems can work together in real-time.